- Home
- Art History
- Aegean Art
Aegean Art
Ancient Aegean Art encompasses achievements of several civilizations that flourished in the Aegean Sea region between approximately 3000-1100 BCE. This rich artistic tradition includes the works of the Cycladic, Minoan, and Mycenaean cultures, each contributing unique elements to the development of early European art.
Cycladic Art
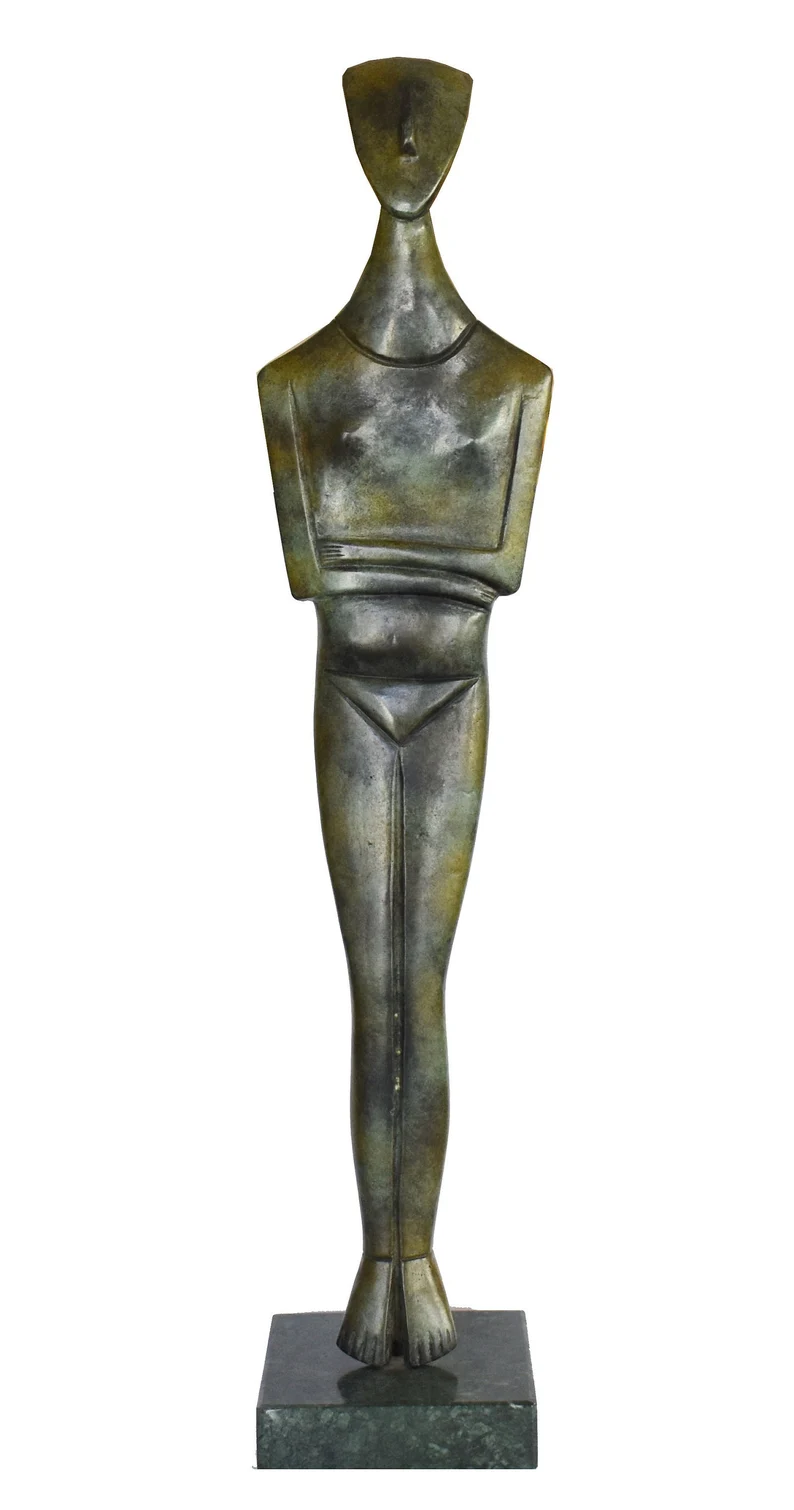 Cycladic Idol
Cycladic IdolThe Cycladic civilization, which developed in the Cyclades Islands, between 2600 BCE and 1100 BCE produced some of the most distinctive sculptures in Ancient Aegean Art. These marble figures, characterized by their simplified, geometric forms and folded-arm postures, have influenced modern artists like Picasso and Modigliani. The most famous of these are the female figures, often referred to as "idol figures," which demonstrate remarkable sophistication in their minimalist design.
Minoan Art
Minoan art, centered on the island of Crete, represents another crucial component of Ancient Aegean Art. The Palace of Knossos, with its elaborate frescoes depicting daily life, religious ceremonies, and natural scenes, provides invaluable insights into Minoan culture. This art history lesson would be incomplete without examining the famous "Bull-Leaping Fresco," which showcases the Minoans' artistic mastery and cultural practices.
 aka: Toreador Fresco aka: Toreador Fresco |
Architecture
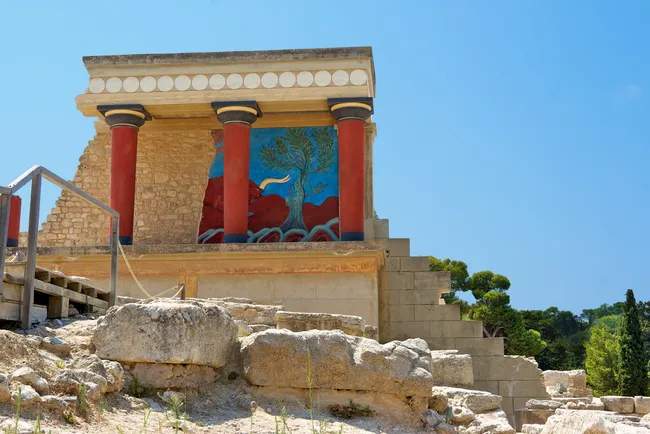 Palace of Minos - ruins. The palace had as many as three stories, with interior staircases built around light and air wells, providing necessary light and ventilation.
Palace of Minos - ruins. The palace had as many as three stories, with interior staircases built around light and air wells, providing necessary light and ventilation.The most well-known structure of Minoan culture is the Palace of Minos at Knossos on the island of Crete. Numerous porticoes, staircases and air shafts give the palace an open, airy quality.
Also known as the Palace of Knossos, located just south of modern-day Heraklion, near the north coast of Crete, was built by a civilization that we call the Minoans. The palace covers about 150,000 square feet, the size of more than two football fields, and was surrounded by a town in antiquity. In the early 20th century it was excavated and restored by a team led by British archaeologist Arthur Evans.
Sculpture
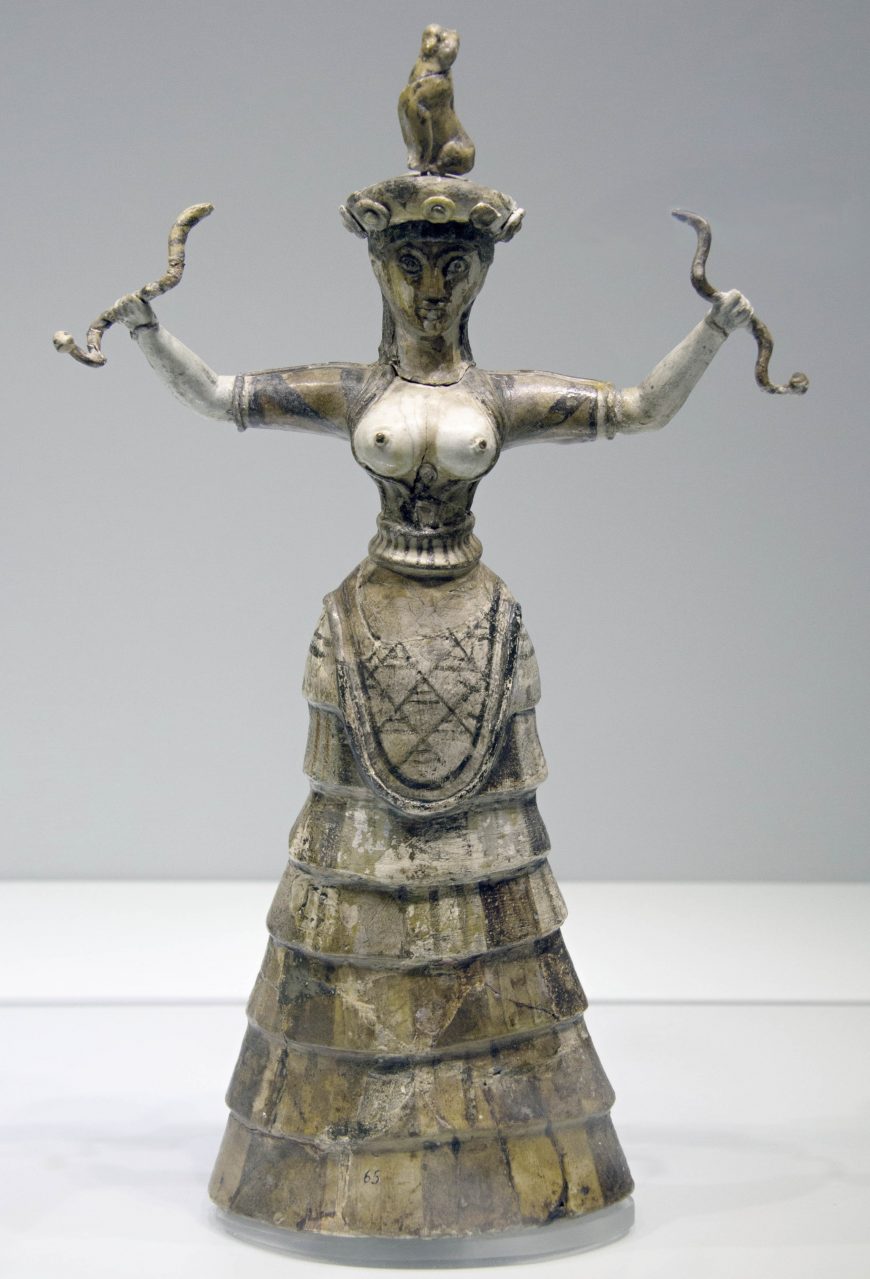 Snake Goddess - from the palace at Knossos. 13-1/2" high.
Snake Goddess - from the palace at Knossos. 13-1/2" high.Minoans produced small figurines known as "snake goddesses." The figurines adhere to a convention of a frontal pose and upraised arms. This form contrasts sharply with the Cycladic idols.
We may speculate the Minoans worshiped a mother goddess whose clothing is typically from the island of Crete, of that era.
Was she their Venus?
Paintings
 "la Parisienne" fresco fragment.
"la Parisienne" fresco fragment.Painting on plastered walls were common in the palaces of the Minoan culture. Besides the Toreador fresco (above), another well-known find is la Parisienne (right).
Her cosmetic prettiness, resembling that of a modern young woman, is the result of the artist's quick hand in painting into wet plaster.
The Minoan painting sense, combining skill with vivacity, are also found in nearby islands in the Aegean Sea.
 fisherman fresco - Santorini island fisherman fresco - Santorini island |
Fresco means "fresh" in Italian. This refers to the practice of painting mineral pigment, dissolved in water, directly on wet lime plaster. As the surface dries, the calcium hydrate in the plaster interacts wit the carob dioxide in the atmosphere, producing calcium carbonate, fusing the pigment to the plaster in a luminous layer. |
Mycenaean Art
The Mycenaean civilization, which flourished on mainland Greece, contributed significantly to Ancient Aegean Art through their architectural achievements, metalwork, and pottery.
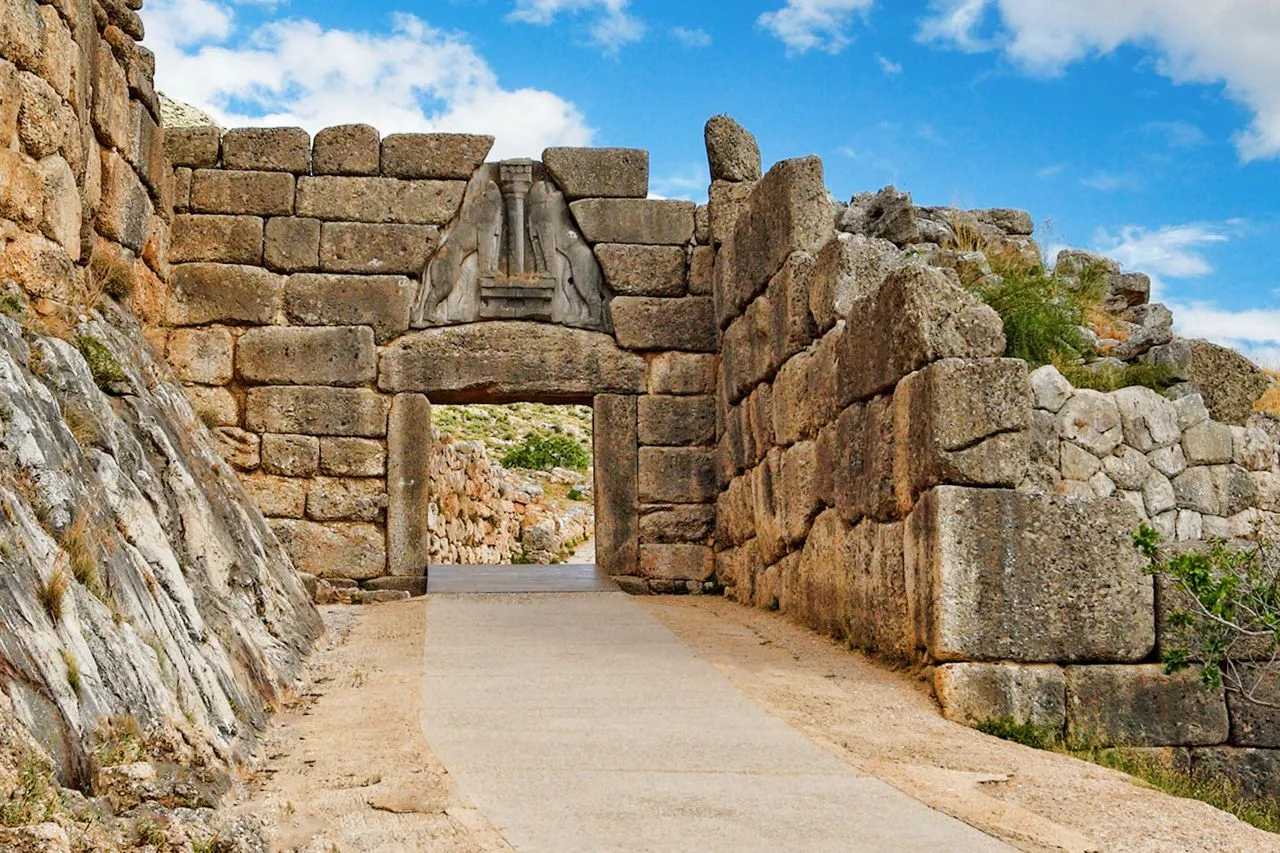 The Lion Gate, Mycenae, c. 1300 BCE. The Lion Gate, Mycenae, c. 1300 BCE. |
 |
The Lion Gate at Mycenae, with its remarkable relief sculpture, stands as a testament to their architectural and artistic prowess. This period's art reflects a more militant society, often featuring scenes of warfare and hunting.
Tombs and their contents
Mycenaeans buried some of their dead in tombs so elaborate as to rival the pharaohs. Such that upon first discovery, one of the beehive tombs was misidentified as the Treasury of Atreus.
 |
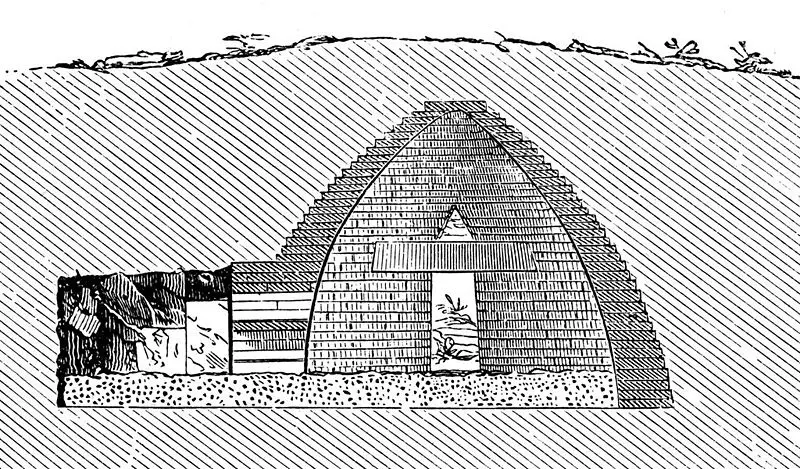 cross-section of beehive tomb cross-section of beehive tomb |
Amongst the finds of ancient royal tombs were found masks of gold and silver place over the face of the mummified deceased. In such tombs could be found drinking vessels, jewelry, weapons, including gold and silver inlaid daggers.
In modest burial sites were found pottery and a few bronze weapons.
The beehive tombs were subject to looting. The burial tradition that preceded beehives was deeper underground burials, in which yielded more artifacts. Amongst the finds were precious metal rhytons and repoussé cups.
Architecture
The architecture of the Mycenae era focused on the fortress concept. They were subject to land invasion, unlike the Minoans on the island of Crete. The Lion Gate is an example of the massive ramparts on a hilltop.
Evidence has not been found of temple architecture by the Mycenaeans.
Sculpture
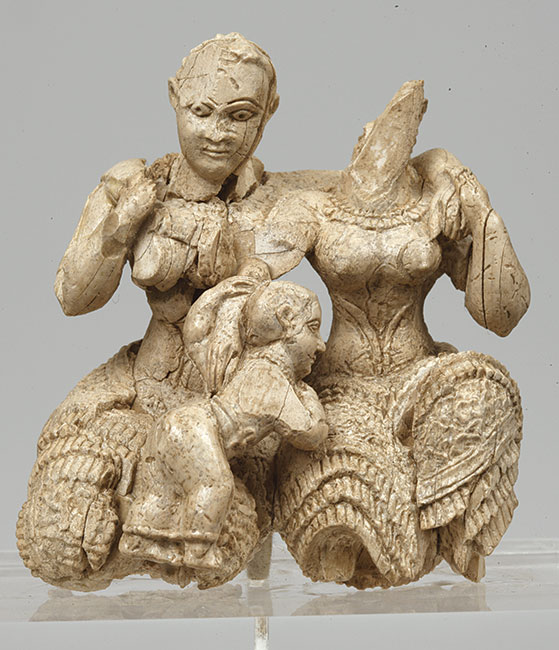

Nevertheless, an ivory sculpture from Mycanae can be surmised to represent some deity or holy family group. Or is this a motherless child-god? The role of such an artwork from c. 1500 BCE in the lives and beliefs of these ancient people is impossible to decipher definitively. These figures who show a familiar affection are an anomaly in the ancient art world in which tenderness is not expressed.
Conclusions
The technical achievements in Ancient Aegean Art are particularly noteworthy, especially in fresco painting and metalworking. The artists developed advanced techniques for creating durable wall paintings and intricate metal vessels, demonstrating a level of sophistication that wouldn't be seen again until the Classical Greek period.
The legacy of Ancient Aegean Art continues to influence contemporary artistic practices and remains a crucial area of study in art history. Understanding these early artistic achievements helps us appreciate the foundations of Western art and the remarkable capabilities of ancient civilizations. This knowledge forms an essential component of any comprehensive art history education.
It's essential to note the distinct characteristics of each civilization's artistic style. The formal elements of Ancient Aegean Art include sophisticated use of color, dynamic movement, and naturalistic representation, particularly in Minoan works. These elements may lead to understanding the development of Western art.
Okay, so now I've put on some ads from Amazon - from which I may earn a few cents. (2025)



